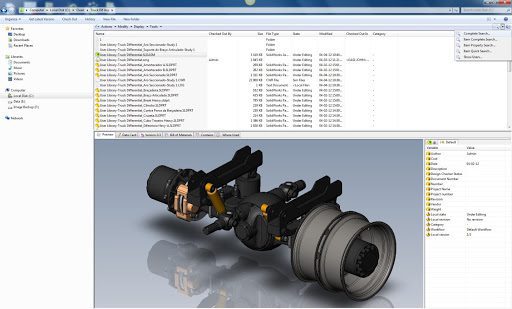
SolidWorks is a comprehensive computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) software developed by Dassault Systèmes, used primarily for mechanical design and simulation. It provides a robust platform for 3D modeling, assembly, and drawing creation. SolidWorks is widely adopted across industries for its powerful tools and user-friendly interface, making it suitable for professionals in fields like mechanical engineering, industrial design, and product development.
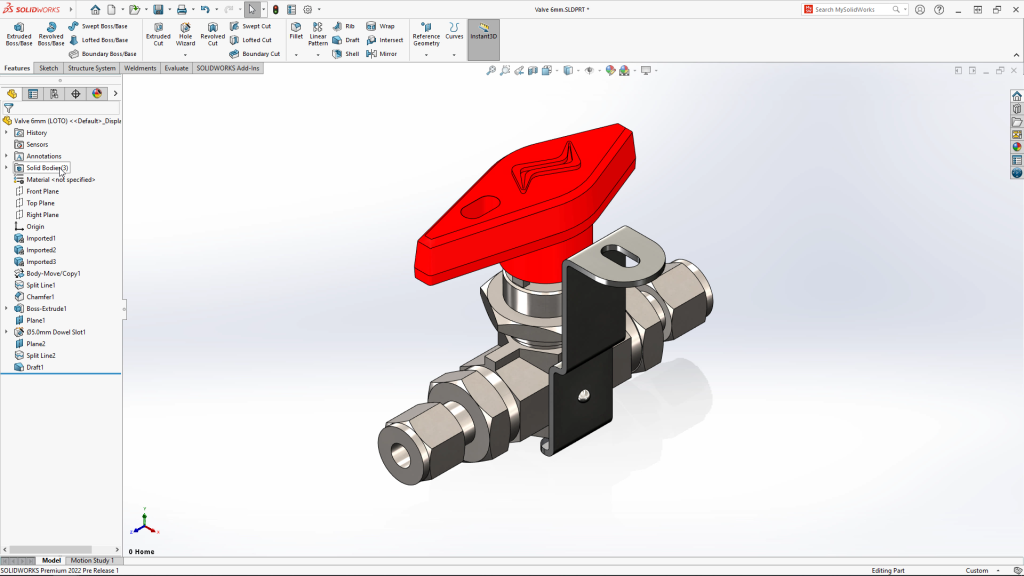
SolidWorks’ range of features and modules makes it a versatile tool for designers and engineers working across different sectors, enabling the creation of complex designs and efficient simulation of real-world performance.