The crankshaft is a part that converts linear motion into rotary motion and vice versa.
The crank system was first invented by Badil Zaman Jezri in 1200 AD. He had used the crank in the water raising device. To get an idea of the spatial shape of the crankshaft, imagine a manual filter. The part of the handle is the same as the crank and its sides (which are aligned) are the supports of the crankshaft. The number of cranks in the crankshaft is proportional to the number of cylinders in an engine. In this way, the piston placed inside each cylinder is connected to one of the crank arms.
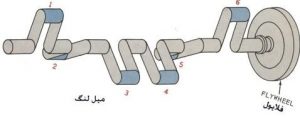
Crankshaft structure Most crankshafts are made of medium carbon steel or alloy steel in combination with chromium and nickel metals and by forging. Of course, in a small number of multi-cylinder engines that work at high speeds, the crankshaft is made using the casting method, which uses relatively large amounts of carbon and copper in its materials. Crankshaft components consist of main shafts, cranks or main crank shafts, crank arms, and balance weights. Cranks Cranks are parts of the crankshaft that are not on the main axis line of the crankshaft (such as an umbrella handle) and the end of the connecting rod is connected to them. The number of cranks in in-line engines is equal to the number of cylinders, and in V-shaped engines, it is half the number of cylinders. The main axes are the axes of the crankshaft that are concentric with the main axis line of the crankshaft. These axes are placed in fixed bearings in the crankcase, and they rotate by relying on them. Each fixed bearing consists of two halves or shafts. The upper half of which is called the fixed half. It is integrally cast with the engine body and in the crankcase, and the lower half is connected by two bolts and nuts in the upper half. Often, the number of crankshaft main axes is different in different engines (even with the same number of cylinders). The crank arms are parts of the crankshaft that connect the main axes of the crankshaft to the cranks, although the crank arms are integrated with the balance weights.